Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Essential Components for Machinery
Deep groove ball bearings are among the most widely used rolling bearings, renowned for their simple yet highly efficient design, playing a pivotal role in various machinery.
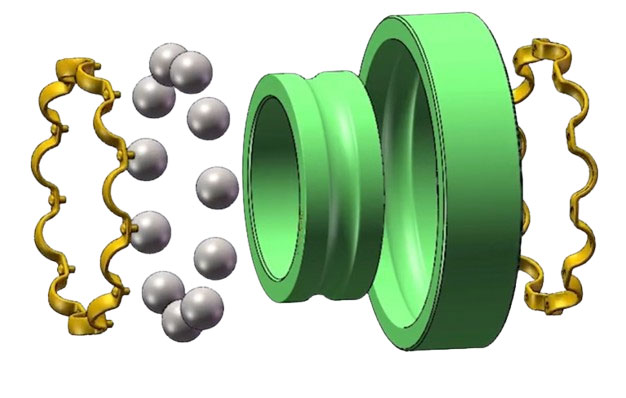
Four Key Components
Inner Ring
- Fitted tightly onto the shaft, it rotates in tandem with the shaft
- Features a smooth raceway for seamless rolling of elements
- Example: In electric motor rotor shafts, transmits power to other components
Outer Ring
- Usually secured within bearing housing or mechanical component holes
- Works with inner ring’s raceway to guide rolling elements
- Example: In automotive wheel hub bearings, supports the wheel’s weight
Rolling Elements (Steel Balls)
- Core elements enabling rolling friction
- Quantity and size vary based on bearing model and load requirements
- Provide stable support for equipment operation
Cage
- Separates steel balls to prevent collisions
- Guides ball movement
- Made from metal or non-metal materials depending on conditions
- Example: Plastic cages used in centrifuge bearings
Raceway Design
Both the inner and outer rings feature semi-circular deep grooves that perfectly match the steel balls. This design evenly distributes loads, allowing the bearing to handle both radial and a certain degree of axial forces, making it suitable for diverse working scenarios.
Sealing and Dust Protection
Dust Cover
- Stamped from steel plates
- Blocks dust in low-dust environments
- Example: Used in fan bearings for office equipment
Seals
- Contact Seals: Fit closely to prevent dust ingress and grease leakage (e.g., automotive engine water pump bearings)
- Non-contact Seals: Use special structure to seal without friction, suitable for high-speed applications in clean environments
Special Structures
Inner Ring with Snap Groove
- Features a groove on the outer ring
- Pairs with snap ring for simplified axial positioning
- Facilitates easier installation and maintenance
Bearing with Filling Slot
- Allows insertion of more steel balls
- Enhances load capacity
- Common in heavy-duty equipment
Double-row Structure
- Combination of two single-row bearings
- Provides higher load-bearing capacity
- Ensures stability in demanding applications